The Curious Case of Animal Crackers: A Deep Dive into Their nutritional Profile
Animal crackers, those whimsical, bite-sized treats shaped like lions, tigers, and bears, have captivated children and adults alike for generations. They evoke nostalgia and bring a touch of playful fun to snack time. But beyond their charming shapes and sweet taste, what exactly lies within these crunchy morsels? Are they a harmless indulgence, or do they harbor hidden nutritional pitfalls? Let’s embark on a comprehensive exploration of animal cracker nutrition, examining their ingredients, macronutrients, micronutrients, and overall impact on our health.
The composition of animal crackers can vary slightly between brands, but the core ingredients generally remain consistent. Here’s a breakdown of the typical components:
Flour: The Base of the Biscuit

Animal crackers primarily rely on refined wheat flour as their base. This provides the bulk of the cracker and contributes to its characteristic texture. However, refined flour is stripped of its bran and germ during processing, resulting in a product that is lower in fiber and certain nutrients compared to whole wheat flour.
Sugar: Sweetening the Deal
Sugar is a prominent ingredient in animal crackers, responsible for their sweet flavor. The type of sugar used can vary, including granulated sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, or other sweeteners. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to numerous health concerns, including weight gain, dental cavities, and increased risk of chronic diseases.
Vegetable Shortening/Oil: Adding Crispness
Vegetable shortening or oil is often added to enhance the texture and crispness of animal crackers. The type of oil used can vary, and some brands may utilize partially hydrogenated oils, which contain trans fats. Trans fats are known to negatively impact heart health by raising LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and lowering HDL (“good”) cholesterol.
Leavening Agents: Creating Lightness
Leavening agents, such as baking soda or baking powder, are used to create a light and airy texture in animal crackers. These agents react with moisture and heat during baking, producing carbon dioxide gas that causes the dough to rise.
Salt: Enhancing Flavor
Salt is added to enhance the flavor of animal crackers. While a small amount of sodium is essential for bodily functions, excessive sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure and other health problems.
Artificial Flavors and Colors: A Touch of Whimsy
Some animal cracker brands may contain artificial flavors and colors to enhance their taste and appearance. The safety and long-term effects of these additives are subject to ongoing debate.
Understanding the macronutrient composition of animal crackers is crucial for assessing their nutritional impact. Here’s a general overview:
Carbohydrates: The Primary Energy Source

Animal crackers are predominantly composed of carbohydrates, primarily from refined flour and sugar. Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, but excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Fats: Contributing to Texture and Flavor
Animal crackers contain a moderate amount of fat, primarily from vegetable shortening or oil. The type and amount of fat can vary between brands, with some containing potentially harmful trans fats.
Proteins: Minimal Contribution
Animal crackers provide a relatively small amount of protein, primarily from the flour. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, but animal crackers are not a significant source of this macronutrient.
Animal crackers are not typically considered a significant source of vitamins and minerals. The processing of refined flour removes many of the nutrients found in whole grains. Some manufactures are adding vitamins and minerals to there product.
Limited Vitamin Content
Due to the use of refined flour, animal crackers generally contain limited amounts of vitamins. Some manufactures will add vitamin enrichments.
Mineral Content: Varies
The mineral content of animal crackers can vary depending on the ingredients and processing methods. Some may contain small amounts of iron, calcium, or other minerals. Read the food label.
Animal crackers, while a beloved treat, should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Here’s a look at some of the potential health implications:
Sugar and Weight Management
The high sugar content of animal crackers can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of obesity, especially when consumed in excess.
Dental Health
The sugary nature of animal crackers can contribute to tooth decay.
Potential for Trans Fats
Some brands of animal crackers may contain trans fats, which are known to negatively impact heart health.
Limited Nutritional Value
Animal crackers are not a significant source of essential nutrients and should not be relied upon as a staple food.
Portion Control
Because animal crackers are small, it is very easy to eat an excessive amount of them. Be aware of the size of your serving.
To make healthier choices when selecting animal crackers, consider the following:
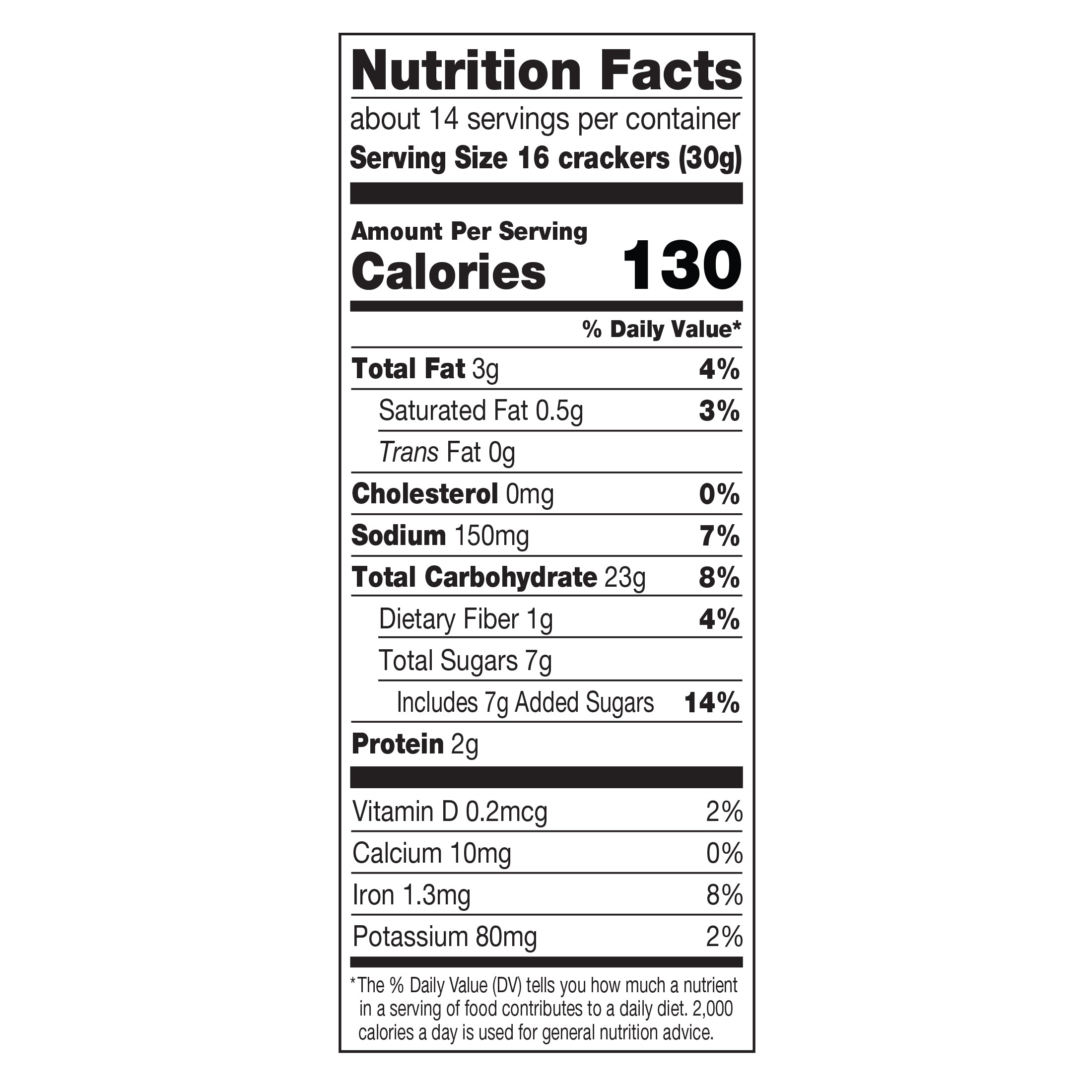
Read the Nutrition Label
Carefully examine the nutrition label to assess the sugar, fat, and sodium content. Pay attention to the serving size and compare different brands.
Choose Brands with Whole Grains
Opt for brands that utilize whole wheat flour or other whole grains, which provide more fiber and nutrients.
Limit Portion Sizes
Enjoy animal crackers in moderation as an occasional treat, rather than a daily staple.
Consider Alternatives
Explore healthier snack alternatives, such as fruits, vegetables, yogurt, or whole-grain crackers.
Animal crackers, while a nostalgic and enjoyable treat, are primarily composed of refined flour and sugar, offering limited nutritional value. They should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, and it’s essential to be mindful of portion sizes and ingredient lists. By making informed choices and prioritizing healthier snack options, we can enjoy the whimsical charm of animal crackers without compromising our well-being.



